Quoted from: https://www.ars.usda.gov/midwest-area/west-lafayette-in/national-soil-erosion-research/docs/wepp/wepp-model-documentation/
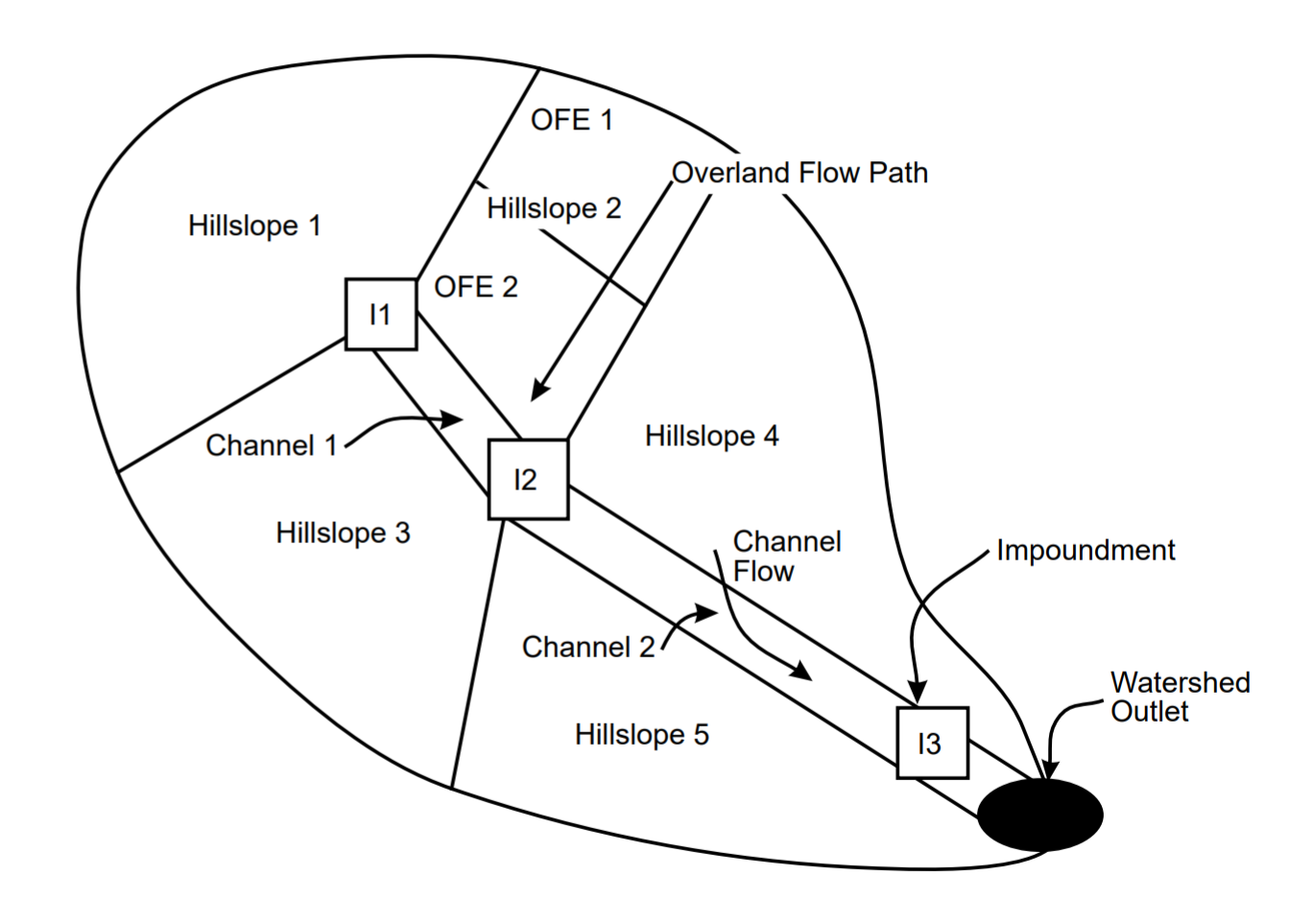
The USDA - Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) model represents a new erosion prediction technology based on fundamentals of stochastic weather generation, infiltration theory, hydrology, soil physics, plant science, hydraulics, and erosion mechanics. The hillslope or landscape profile application of the model provides major advantages over existing erosion prediction technology. The most notable advantages include capabilities for estimating spatial and temporal distributions of soil loss (net soil loss for an entire hillslope or for each point on a slope profile can be estimated on a daily, monthly, or average annual basis), and since the model is process-based it can be extrapolated to a broad range of conditions that may not be practical or economical to field test. In watershed applications, sediment yield from entire fields can be estimated. Figure 1.1.1 depicts a small watershed on which the WEPP erosion model could be applied.

Figure 1.1.1 Schematic of a small watershed which the WEPP erosion model could be applied to. Individual hillslopes (1 to 5), or the entire watershed (composed of 5 hillslopes, 2 channel segments, and 3 impoundments) could be simulated.
Processes considered in hillslope profile model applications include rill and interrill erosion, sediment transport and deposition, infiltration, soil consolidation, residue and canopy effects on soil detachment and infiltration, surface sealing, rill hydraulics, surface runoff, plant growth, residue decomposition, percolation, evaporation, transpiration, snow melt, frozen soil effects on infiltration and erodibility, climate, tillage effects on soil properties, effects of soil random roughness, and contour effects including potential overtopping of contour ridges. The model accommodates the spatial and temporal variability in topography, surface roughness, soil properties, crops, and land use conditions on hillslopes.
In watershed applications, the model allows linkage of hillslope profiles to channels and impoundments. Water and sediment from one or more hillslopes can be routed through a small fieldscale watershed. Almost all of the parameter updating for hillslopes is duplicated for channels. The model simulates channel detachment, sediment transport and deposition. Impoundments such as farm ponds, terraces, culverts, filter fences and check dams can be simulated to remove sediment from the flow.