A physically based snow module is developed to simulate the snow accumulation, melt and runoff generation processes. This module is coupled with a distributed geomorphology- based eco-hydrological model (GBEHM) In the GBEHM, the basin is divided into different sub-basins that contain discrete flow intervals. Each flow interval is connected by several topographically similar ’hillslope-valley’ grids. Each grid has different land types, such as vegetation, snowpack, glacier, soil and aquifer. The runoff from each grid includes surface flow, lateral flow and ground flow. In the GBEHM, the grid runoff is first transferred into the flow interval and then into the river channel from different pathways. The most important improvement of our module is that the snowmelt paths are separately traced in each calculation step, which make the evaluation of snowmelt contribution more reasonable. Another improvement is that the physically based snowmelt module is coupled with a geomorphology-based hy-drological model, which extends the simulation capacity of snowmelt at basin-scale hy-drological processes. In terms of the snow module at vertical dimension, the physical schemes including heat and water balance are similar with SNTHERM model[Jordan,1991], SNOWPACK model[BarteltandLehning, 2002] and CROCUS model[Vionnetetal., 2012].
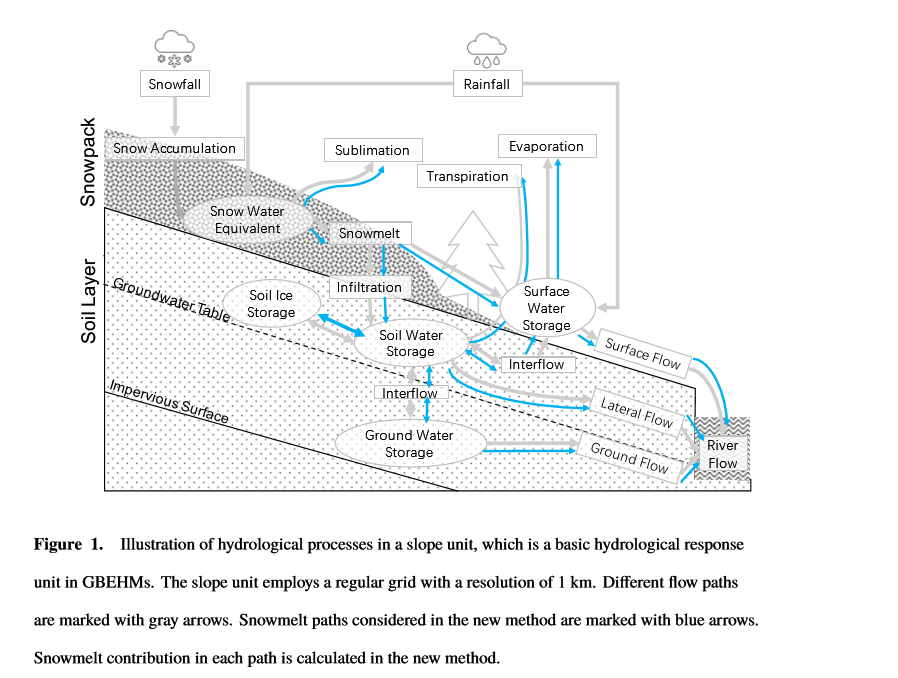
In the original GBEHM model, it is difficult to distinguish the snowmelt compo- nent from total water component, because liquid water from different sources is mixed and transferred in simulating these hydrological processes. Here, we introduce a detailed separation method to determine the snowmelt contribution and pathway in the runoff gen- eration processes (Figure 1). The proportion of snowmelt water in soil layers, aquifers and different types of flow are updated after the calculation of soil moisture movement and evapotranspiration. In the new separation method, the snowmelt water proportions in snowpack, in each soil layers and in each aquifer are iteratively calculated, and the contri- bution of snowmelt to total discharge is calculated.