Basic Information
MEGAN is a modeling system for estimating the emission of gases and aerosols from terrestrial ecosystems into the atmosphere. Driving variables include landcover, weather, and atmospheric chemical composition. MEGAN is a global model with a base resolution of ~ 1 km and so is suitable for regional and global models. A FORTRAN code is available for generating emission estimates for the CMAQ regional air quality model. The algorithms have also been incorporated as an on-line component in several regional and global chemistry and transport models. Global distributions of landcover variables (Emission Factors, Leaf Area Index, and Plant Functional Types) are available for spatial resolutions ranging from ~ 1 to 100 km and in several formats (ARCGIS, netcdf). Regional distributions are are available at resolutions from 30m to 1000m.
It should be noted that running this version of MEGAN requires both access to and knowledge of a Unix operating system and working knowledge of FORTRAN. If you need to regrid the MEGAN input files then you will also need knowledge/access to Python computer language, ESRI ArcMAP software (or some alternative regridding software), FORTRAN. Users who have never been exposed to Unix-type operating systems (i.e., if you are only familiar with Windows) will need to learn Unix to run MEGAN. Although you do not need to be a computer programmer to run the model, you should have a basic understanding of computer programming and Unix (i.e., you should know how to unzip/untar files and other basic commands in Unix, install libraries and link files within Unix, and know basic FORTRAN commands such as how to invoke a code). If you need to regrid landcover data then you should also be familiar with (and have access to) ArcMAP or a similar program. In summary, you should have a working knowledge of ArcMap, Unix, FORTRAN, and Python before attempting to use MEGAN. We have listed links to information and resources in the top left sidebar of this page that we hope will be helpful to those individuals interested in learning more about the tools and programs necessary to run MEGAN.
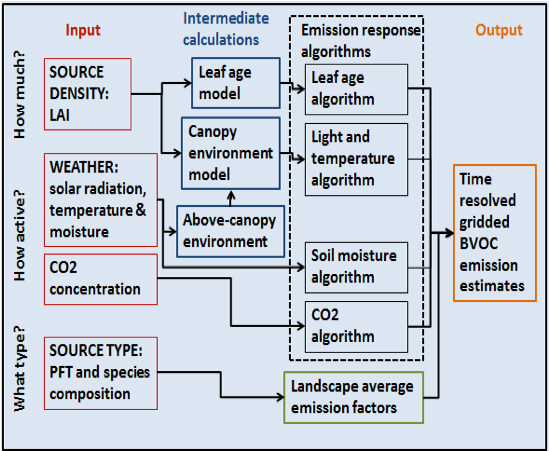 Schematic of MEGAN2.1 model components and driving variables.
Schematic of MEGAN2.1 model components and driving variables.
MEGAN Overview
MEGAN is a semi-mechanistic model that accounts for the major known processes controlling biogenic emissions. MEGAN estimates only emissions of known compounds and includes additional compounds whenever they are identified as being of potential interest for the atmosphere. Emissions of 150 chemical species are included in MEGANv2.1 and the model can output individual compounds or categories associated with various atmospheric chemistry schemes. The 150 compounds are lumped into 20 categories based on how emissions vary in response to changes in environmental conditions. Emission variations are first estimated for the 20 categories and then speciated into the 150 compounds or output in chemical categories associated with common atmospheric chemistry schemes (e.g., CB4, CB05, CB6, SAPRC99, MOZART, SOAX). Driving variables include land cover, weather, and atmospheric chemical composition. The MEGAN code and input files are available at no cost. User’s Guides, models and input files are provided at http://lar.wsu.edu/megan/guides.html.
MEGANv2.1 accepts PFT/LAI/EF MAP data in ASCII format and meteorological data in netcdf/ioapi format. The native outputs are in netcdf/ioapi format. The UAM-CAMx emission 2D format is optional with conversion processor. MEGAN can be run on a number of 4 32bit or 64bit LINUX/Unix operating system. Users may need to make changes in compliers and environmental settings to get it run on their own machines. MEGAN was originally written as an ACCESS-VBA code by Alex Guenther. Jack Chen (Washington State University- now at NRC-Canada) developed the initial FORTRAN framework and I/O formats for MEGAN version 1.0. MEGAN Versions 2.00 to 2.04 were written in FORTRAN by Tanarit Sakulyanontvittaya (University of Coloradonow at ENVIRON). MEGAN version 2.10 was written by Xuemei Wang (Sun-Yat Sen University) and Tan Sakulyanontvittaya (ENVIRON).
MEGAN Software / Operating System Prerequisites
It should be noted that running this version of MEGAN requires both access to and knowledge of a LINUX/UNIX operating system and working knowledge of FORTRAN. Users who have never been exposed to Unix-type operating systems (i.e., if you are only familiar with Windows) unfortunately will find it difficult to run MEGAN. Although you do not need to be a computer programmer to run the model, you should have a basic understanding of computer programming and Unix (i.e., you should know how to unzip/untar files and other basic commands in Unix, install libraries and link files within Unix, and know basic FORTRAN commands such as how to invoke a code). If you need to regrid the MEGAN input files then you will also need either 1) knowledge/access to Python computer language and ESRI ArcMAP software or 2) use a FORTRAN based preprossor for regridding the input files. In summary, you should have a working knowledge of Unix and FORTRAN (and possibly ArcMap and Python for regridding input files) before attempting to use MEGAN.
The following are the system and software requirements for installing and running MEGAN 2.10:
• LINUX/UNIX operating system
• csh/sh scripting language
• FORTRAN 90 compiler, i.e. pgi
• It can only be run on a single processor, no MPI support
• Netcdf 3.6.0 or greater • ioapi 3.1
• MCIP 3.6
It has been successfully tested on GNU/Linux x86_64 machine with PGI compiler. The provided test case was also created on GNU/Linux x86_64 machine.


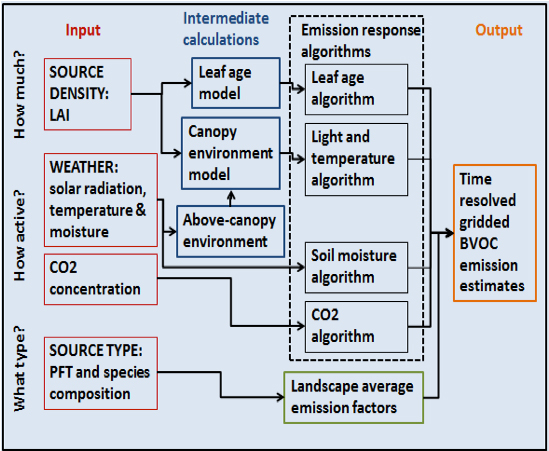
 Schematic of MEGAN2.1 model components and driving variables.
Schematic of MEGAN2.1 model components and driving variables.