Quoted from: https://www.pnnl.gov/projects/distributed-hydrology-soil-vegetation-model
The Distributed Hydrology Soil Vegetation Model, or DHSVM, is a spatially distributed, physics-based hydrology model developed in the early 1990s (Wigmosta et al., 1994) by PNNL and the University of Washington. It has since been extensively applied worldwide and referenced in over 1,700 publications.
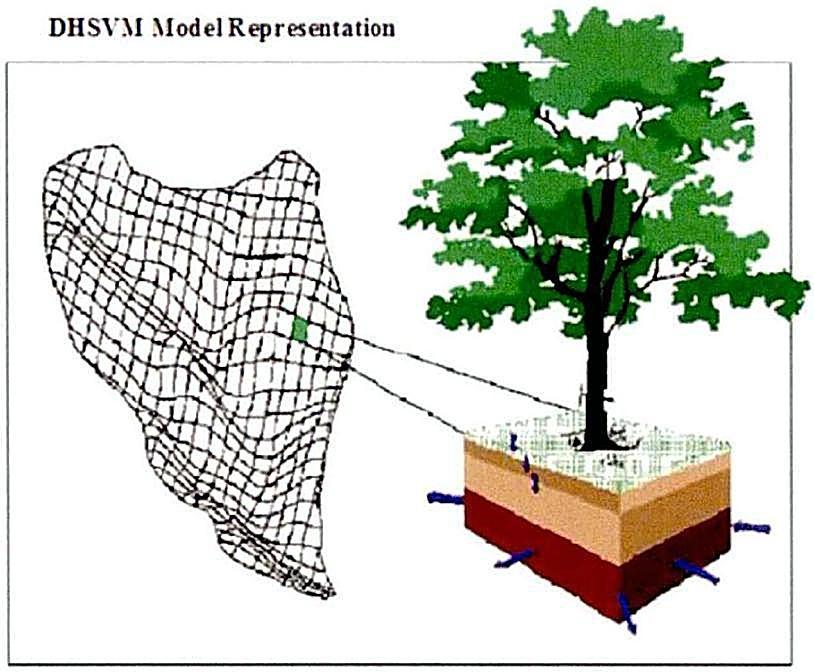
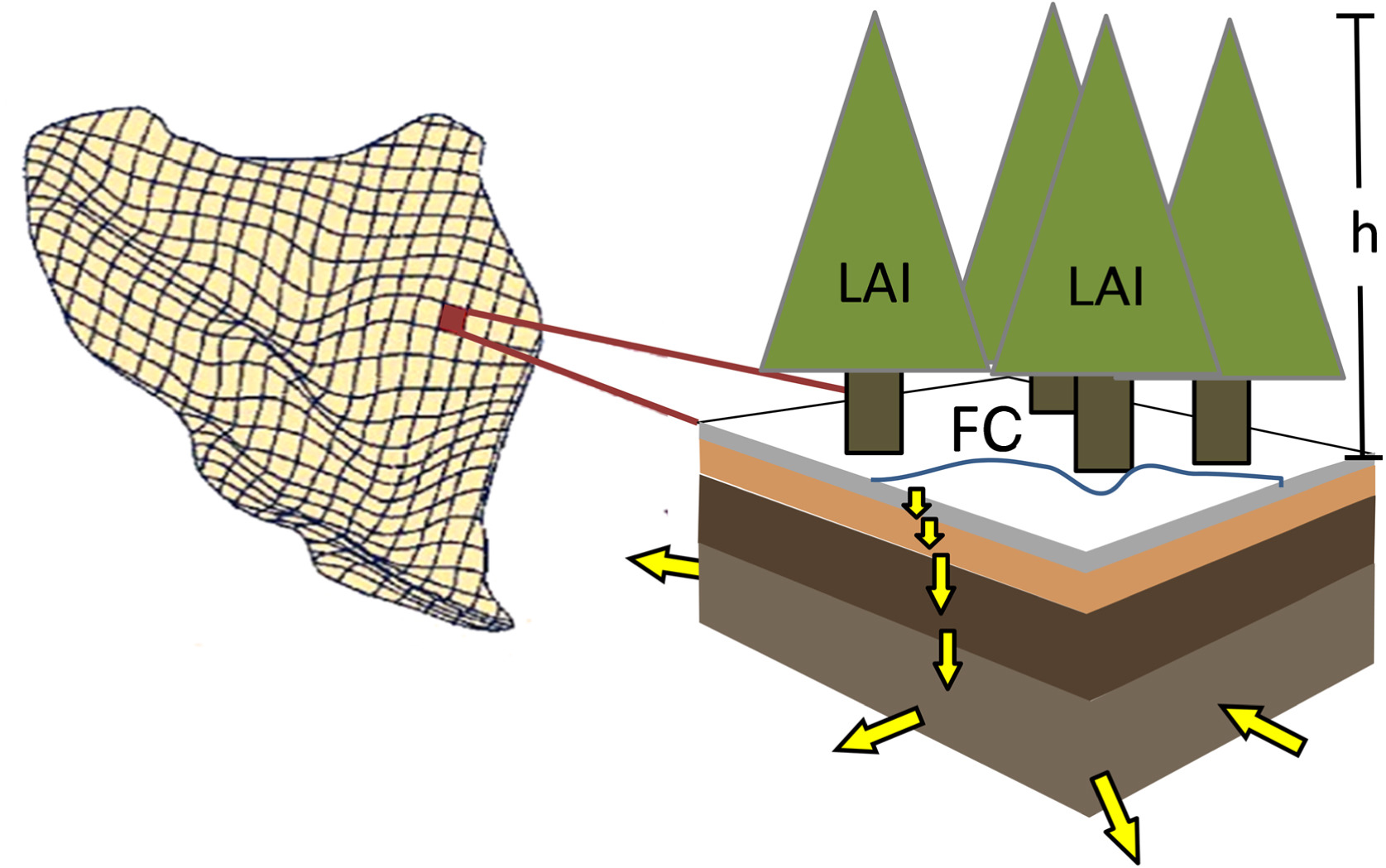
With high spatial resolution, DHSVM explicitly represents the effects of local climate, topography, soil, and vegetation on snow accumulation and melt along with overland and subsurface hydrological processes within watersheds. The model is typically applied at spatial resolutions ranging from 10 meters to the order of 100 meters, and at sub-daily timescales for multi-year simulations.
Originally, DHSVM was applied predominantly to mountainous watersheds for modeling mountain hydrology in forested environments. To advance scientific understanding of the processes and dynamics related to hydrology and water resources in diverse settings, DHSVM has been further developed by PNNL, the University of Washington, and the greater user community. Subsequent developments have extended the capability of DHSVM to simulate urban hydrology, glacio-hydrological dynamics, river thermal dynamics, urban water quality, erosion and sediment transport, and forest-snow interactions in canopy gaps. More recently, the DHSVM code has been parallelized for distributed memory computers, which remarkably enhances simulation speed in large-scale applications, such as the Columbia River Basin with a drainage area of 668,000 km2 .
Please visit the DHSVM GitHub page to download the latest version. Information on model development and model applications in a wide range of topics are provided in the publication section.