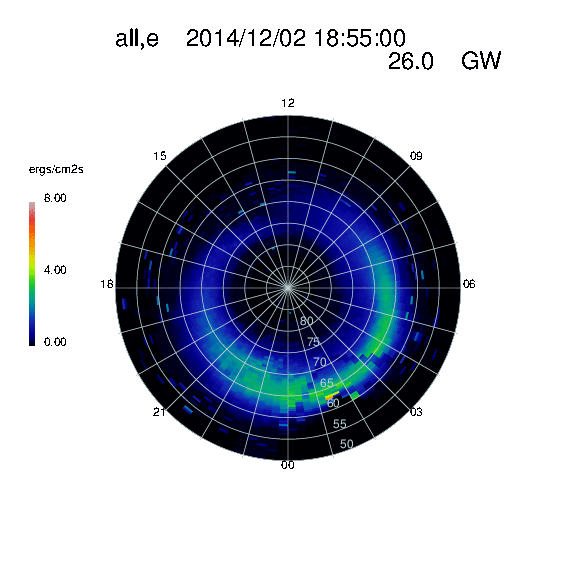
Quoted from: https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/models/modelinfo.php?model=Ovation%20Prime
Model Description
The OVATION Prime model was developed using energetic particle measurements from the polarorbiting Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites and considers four types of aurorae: two types of discrete electron aurorae (1A: monoenergetic and 1B: broadband) and two types of diffuse aurorae (2A: electron and 2B: ion) [Newell et al., 2010]. The OVATION Prime model is written in IDL and was developed at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (JHU-APL) by Patrick Newell and co-workers. The model may be freely downloaded from SourceForge.
Ovation Prime provides statistical distribution of auroral precipitation in the ionosphere obtained from 11 years of DMSP electrostatic analyzer data. Observations have been binned by magnetic local time and latitude and by solar wind parameters (Vx, By, Bz, N).
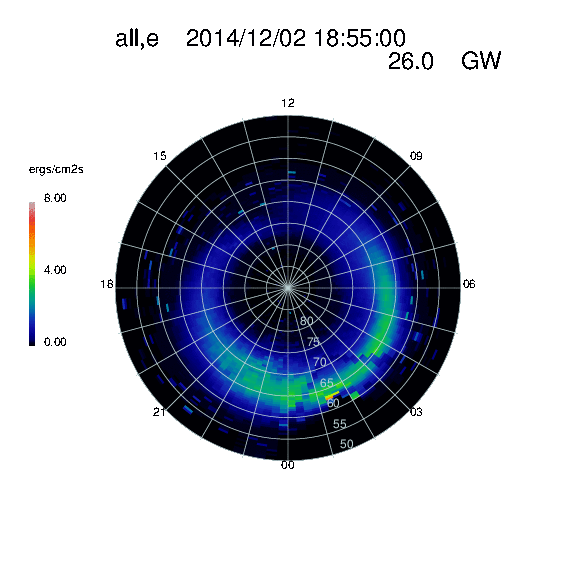
CCMC services available: Model runs in real time using ACE real time solar wind data. Images feed iSWA cygnets.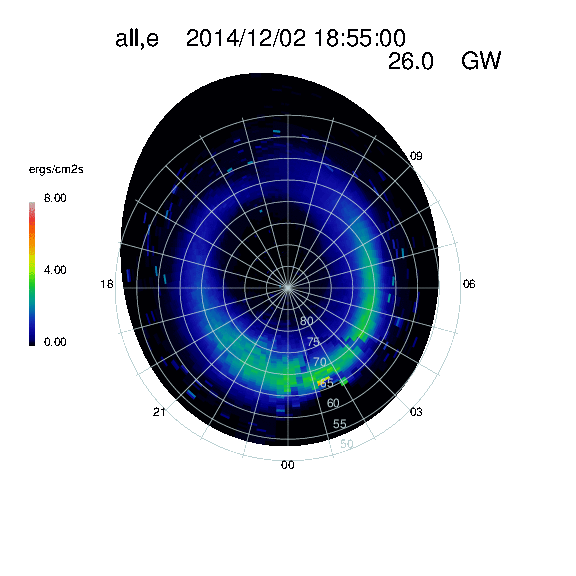
Title in cygnet images type of precipitation included
all,e: 1A, 2B, 2A
ions,i: 2B
all,e+i: all four (1A, 1B, 2A, 2B)
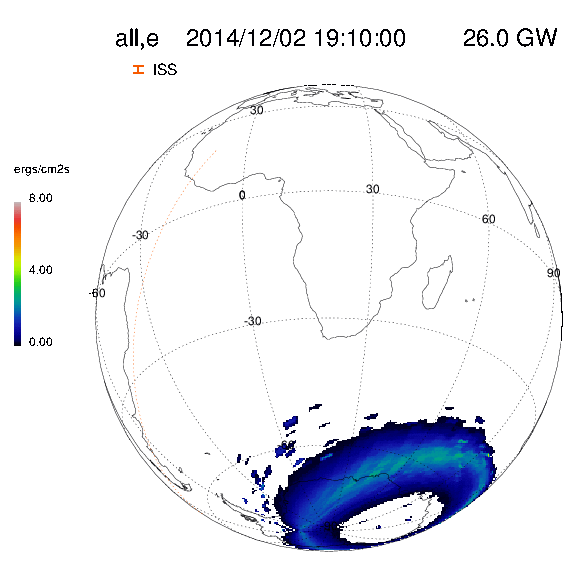
Eight cygnets exist for each of the above combinations of precipitation patterns (see example layout images):
Magnetic coordinates (one cygnet): Polar view in northern hemisphere (upper left)
Geographic views (7 cygnets): North Amercia, Europe, Asia (remaining in top row of images)
North Pole, South America, South Africa, Australia (bottom row of images)
References and relevant publications
Machol, J. L., J. C. Green, R. J. Redmon, R. A. Viereck, and P. T. Newell (2012), Evaluation of OVATION Prime as a Forecast Model for Visible Aurorae, Space Weather, 10, S03005, doi:10.1029/2011SW000746.
Newell, P.T., T. Sotirelis, K. Liou, C.-I. Meng, and F.J. Rich (2007), A nearly universal solar windmagnetosphere coupling function inferred from 10 magnetospheric state variables, J. Geophys. Res., 112, A01206, doi:10.1029/2006JA012015.
Newell, P. T., T. Sotirelis, and S. Wing (2009), Diffuse, monoenergetic, and broadband aurora: The global precipitation budget, J. Geophys. Res., 114, A09207, doi:10.1029/2009JA014326.
Newell, P. T., T. Sotirelis, and S. Wing (2010), Seasonal variations in diffuse, monoenergetic, and broadband aurora, J. Geophys. Res., 115, A03216, doi:10.1029/2009JA014805.
Sotirelis, T. and P. T. Newell (2000), "Boundary-oriented electron precipitation model," J. Geophys. Res., 105 (A8), 18,655-18,673.
Relevant links
http://sourceforge.net/projects/ovation-prime/
iSWA: Example: layout for Electrons:
http://iswa.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?i_1=451&l_1=33&t_1=302&w_1=500&h_1=510&s_1=0_0_10_3&i_2=453&l_2=39&t_2=827&w_2=500&h_2=510&s_2=0_0_10_3&i_3=503&l_3=1569&t_3=305&w_3=500&h_3=510&s_3=0_0_10_3&i_4=507&l_4=1063&t_4=829&w_4=500&h_4=510&s_4=0_0_10_3&i_5=508&l_5=555&t_5=829&w_5=500&h_5=510&s_5=0_0_10_3&i_6=509&l_6=1061&t_6=304&w_6=500&h_6=510&s_6=0_0_10_3&i_7=455&l_7=552&t_7=300&w_7=500&h_7=510&s_7=0_0_10_3&i_8=506&l_8=1572&t_8=828&w_8=500&h_8=510&s_8=0_0_10_3
CCMC Contact(s)
Lutz Rastaetter, Yihua Zheng
301-286-9571
Developer Contact(s)
Patrick Newell