Quoted from: https://www.fema.gov/hazus
Hazus is a nationally applicable standardized methodology that contains models for estimating potential losses from earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes. Hazus uses Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology to estimate physical, economic, and social impacts of disasters. It graphically illustrates the limits of identified high-risk locations due to earthquake, hurricane, flood, and tsunami. Users can then visualize the spatial relationships between populations and other more permanently fixed geographic assets or resources for the specific hazard being modeled, a crucial function in the pre-disaster planning process.
Hazus is used for mitigation and recovery, as well as preparedness and response. Government planners, GIS specialists, and emergency managers use Hazus to determine losses and the most beneficial mitigation approaches to take to minimize them. Hazus can be used in the assessment step in the mitigation planning process, which is the foundation for a community's long-term strategy to reduce disaster losses and break the cycle of disaster damage, reconstruction, and repeated damage. Being ready will aid in recovery after a natural disaster.
Potential loss estimates analyzed in Hazus include:
- Physical damage to residential and commercial buildings, schools, critical facilities, and infrastructure;
- Economic loss, including lost jobs, business interruptions, repair, and reconstruction costs;
- Social impacts, including estimates of shelter requirements, displaced households, and population exposed to scenario floods, earthquakes, and hurricanes, and tsunamis
As the number of Hazus users continues to increase, so do the types of uses. Increasingly, Hazus is being used by states and communities in support of risk assessments that perform economic loss scenarios for certain natural hazards and rapid needs assessments during hurricane response. Other communities are using Hazus to increase hazard awareness.
Quoted from: http://www.appsolutelydigital.com/ModelPrimer/chapter1_section1.html
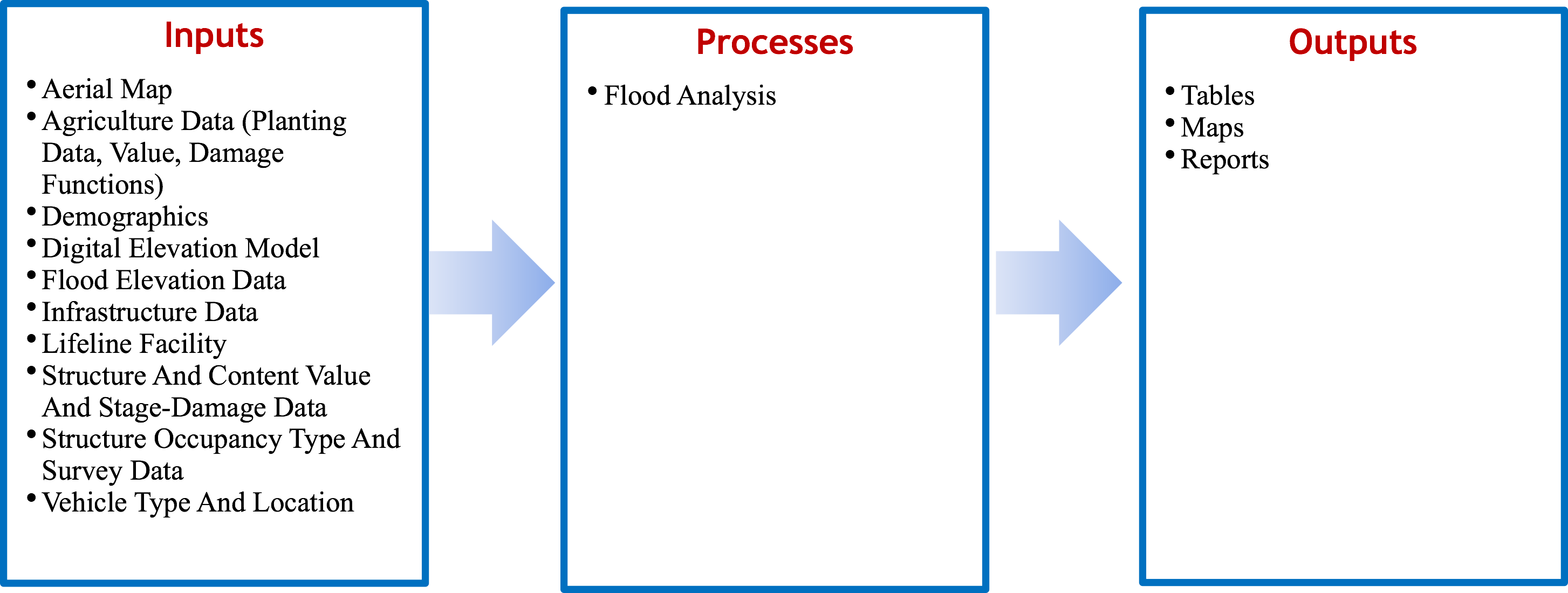
HAZUS-MH (Hazard United States – Multi Hazard), first released in 1997, uses a standardized methodology to estimate physical, economic and social impacts of disasters from earthquakes, floods, hurricanes and high winds. Specifically, HAZUS-MH estimates impacts by overlaying the spatial locations of potential hazards with structures, population, vehicles, utilities, etc., in ArcGIS. HAZUS-MH, as part of its vulnerability assessment, creates relationships using hydrology, hydraulic, and economic data to create relationships between annual exceedance probability and peak discharge, discharge and stage, and stage and damage. The program has been applied in flood mitigation, policy- making, planning or zoning, emergency planning and response, and to estimate sectoral economic impacts. The key feature of the HAZUS-MH software is an extension to ArcGIS that allows for pre-processing and visualization of outputs. HAZUS allows for three levels of analysis (basic to advanced) depending on data availability.
Advantages
- Compare and analyze various alternatives
- Calculate economic and societal impacts
- Calculate hurricane, earthquake, and wind damages
- Developed technical and user manual
- Proof of concept demonstrates international use
- Estimate debris volume
- Technical support provided virtually or via an in- person training class
- Determines if lifeline facility will be impacted
- Determines flooding impact from coastal or riverine systems or both
Limitations
- Hydraulic analysis within model is based on Manning’s Equation; doesn’t account for backwater effect
- Program data and maps developed for US; international maps and databases will have to be developed
- Inability to estimate loss of life
- Requires broad range of disciplines
- No accounting for uncertainty
- Not applicable for flash floods









