Quoted from: https://www.pml.ac.uk/Modelling_at_PML/Models/ERSEM
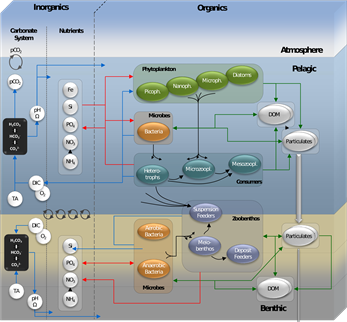
ERSEM (European Regional Seas Ecosystem Model), has grown in scale and scope in recent years. It addresses biogeochemical and ecological systems in many applications in global regional seas and more recently the global ocean, engaging in a range of problem solving, predictive and impact studies.
Its strength and uniqueness lies in its ability to define relatively complex ecosystems in both pelagic and benthic environments. ERSEM is one of the few marine ecosystem models that uses variable stoichiometry and includes the microbial foodweb, and the major biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and silicate. Recent revisions mean the ERSEM model now includes the iron cycle, calcification, a light model based on inherent optical properties and a more detailed representation of the microbial loop.
ERSEM is an ideal system with which to assess how the changing environment (e.g. light availability, nutrient inputs, temperature, pH) impacts ocean productivity, community size structure, trophic transfer and elemental cycles. ERSEM simulates low to mid trophic levels and can be used to drive fisheries and aquaculture models.
ERSEM is routinely coupled to a wide variety of hydrodynamic models such as GOTM, NEMO and FVCOM using a coupling interface called FABM which enables ERSEM to be run as a simple box model or more realistically in 1-3 dimensional space at scales ranging from local, and coastal via regional to global applications.
Since its original development as a European initiative in the early nineties ERSEM has evolved significantly from a coastal ecosystem model for the North-Sea to a generic tool for ecosystem simulations from shelf seas to the global ocean. It is a UK community model which is also widely used internationally. The development of ERSEM is led by PML and has more than registered 300 users from 30 countries across the world and has appeared in more than 200 peer-reviewed publications.
The recently released version of ERSEM will increase the capability of users by enabling comprehensive studies of the lower trophic levels of the marine ecosystem across the globe under present day and future conditions in one single framework, thus providing an ideal platform for research, operational forecasting and projections of future climate change. Distribution of ERSEM is accompanied by a testing framework enabling the analysis of individual parts of the model.
Related publications
The following publication provides a full description of the ERSEM model.
- ERSEM 15.06: a generic model for marine biogeochemistry and the ecosystem dynamics of the lower trophic levels. Momme Butenschön et al. 2016. Geosci. Model Dev., 9, 1293-1339, 2016
doi:10.5194/gmd-9-1293-2016